Xiaolei Zhang
Queen’s University Belfast, UK
Title: Theoretical elucidation of the molecular behaviour of levoglucosan during biomass pyrolysis
Biography
Biography: Xiaolei Zhang
Abstract
The bio-fuels and bio-chemicals derived from lignocellulosic biomass are popularly referred to as second-generation bio-fuels or bio-chemicals. As a valuable chemical material, levoglucosan is one important primary product during cellulose pyrolysis either as an intermediate or as a product. The fundamental investigation on the mechanism and kinetic modelling of the production of levoglucosan from lignocellulosic biomass has been carried out. Three available mechanisms for levoglucosan formation have been studied theoretically by performing density functional theory based calculations. Specifically, the molecular behaviour of levoglucosan has elucidated by revealing 14 reaction pathways, 26 elemental reaction steps, and the involved around 60 compounds act as intermediates, transition states, or products. By comparing with the activation energy obtained from the experimental results, it was concluded that levoglucosan chain-end mechanism fits better with the experimental data for the formation of levoglucosan. The variational transition state rate constants for every elementary reaction and every pathway were calculated. The first-order Arrhenius expressions for these elementary reactions and pathways were suggested. Furthermore, this research provides techno-economic assessment of the available routes for the production of levoglucosan and its derived products, and the paper will be concluded by identifying key challenges and future trends for second-generation bio-chemicals. It also confirms that Quantum Mechanics based simulation can reveal fundamental phenomena, which are difficult to be explored from traditional experimental techniques, and can be used to guide the experimental design and industrial application.
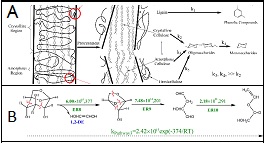
Recent Publications:
- Zhang, X. (2016), Essential scientific mapping of the value chain of thermochemical converted second-generation bio-fuels. Green Chemistry. 18, 5086-5117
- Zhang, X., Kumar, A., Oestreich, D., Arnold, U., and Sauer, J. (2016). An optimization process design for woody biomass gasification with further upgrading into oxymethylene ethers. Biomass and Bioenergy. 90, 7–14.
- Zhang, X., Yang, W. and Blasiak, W. (2013). Kinetics Study on Thermal Dissociation of Levoglucosan during Cellulose Pyrolysis. Fuel, 109, 476–483.
- Zhang, X., Yang, W. and Blasiak, W. (2013). Levoglucosan Formation Mechanisms during Cellulose Pyrolysis. Journal of Analytical and Applied Pyrolysis, 104, 19–27.
- Zhang, X., Yang, W. and Blasiak, W. (2012). Kinetics of levoglucosan and formaldehyde formation during cellulose pyrolysis process. Fuel, 96(0), 383–391.


