Ralph-Uwe Dietrich
German Aerospace Center, Germany
Title: Alternative fuels from Biomass and Power (PBtL) – A case study on process options, technical potentials, fuel costs and ecological performance
Biography
Biography: Ralph-Uwe Dietrich
Abstract
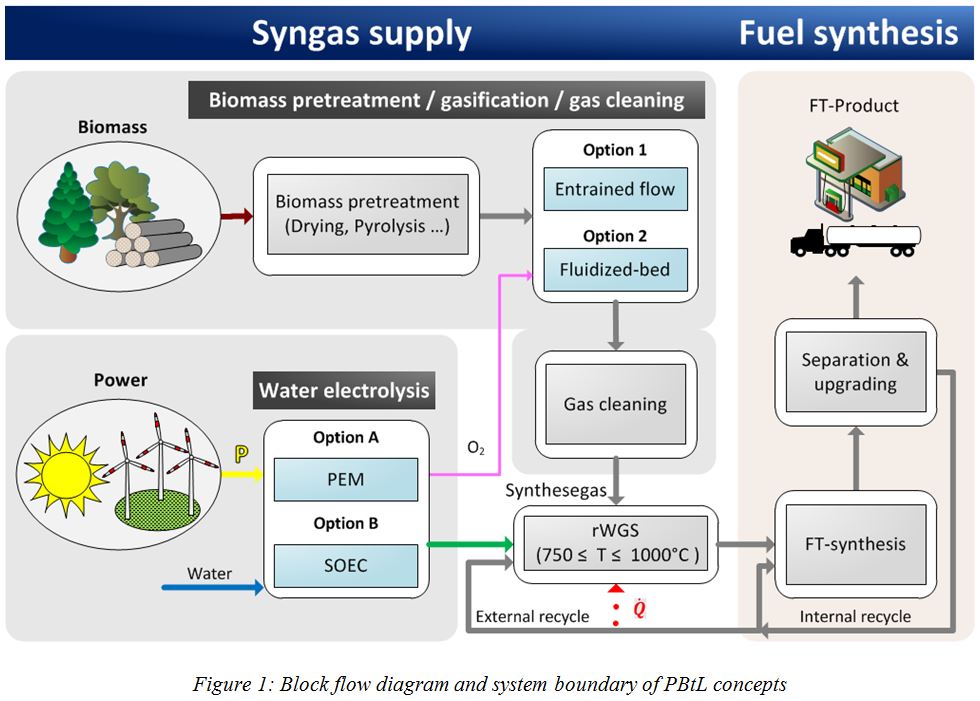
Greenhouse gas emissions in the transport sector shall be reduced to reach globally agreed COP21 goals. One option is to replace fossil based fuels with bio-based alternatives. The technical potential of biofuels made from energy crops (1st generation), biomass and waste wood (2nd generation) typically suffer from the limited technical potential of biomass resources in central Europe. Biofuel output can significantly be increased in the Power&Biomass-to-Liquid (PBtL) concept utilizing renewable electricity in modified BtL plants. The case study presents detailed results on promising process configurations of Fischer-Tropsch PBtL concepts based on different gasifiers and electrolyzers in terms of fuel production potentials, fuel costs and CO2 footprint.
Results from the study indicate that the biomass specific fuel output can be quadrupled when utilizing green electricity for hydrogen generation in the PBtL process. The increased fuel output results in lower fuel production costs due to the effects of the economy of scale. Fuel production costs below 1.3 €/l were estimated for a large PBtL plant (225 kt/year) assuming an electricity price of 31.4 €/MWh (average EEX-Phelix index of the year 2015). The exergy analysis reveals that the electrolysis and the gasification processes are characterized by the most significant thermodynamic optimization potentials. The PBtL concept is characterized by a lower CO2 footprint, as high carbon conversion rates close to 100 % can be achieved by using oxy-fuel technology and recycling the entire CO2 within the system. Hence, largest CO2 emissions arise from harvesting and transportation of the biomass feedstock.
Recent Publications:
- Albrecht, F, König, D, Baucks, N, Dietrich, R.-U. (2017) A standardized methodology for the techno-economic evaluation of alternative fuels – A case study. Fuel – The Science and Technology of Fuel and Energy, 194:511-526.
- Albrecht, F, Zhang, J, Dietrich, R.-U. (2016) Process design and economic assessment of converting CO2 to liquid fuels. ACI's 7th Carbon Dioxide Utilisation Summit 2016, 19.-20. Okt. 2016, Lyon, France.
- Albrecht, F, Dietrich, R.-U., König, D, Seitz, A, Thess, A (2016) Techno-Economic Assessment of the Production of Synthetic Jet Fuel from Carbon Sources and Renewable Hydrogen. GREENER AVIATION 2016, 11.-13. Oct. 2016, Brussels, Belgium
- Albrecht, F, König, D, Dietrich, R.-U. (2016) The potential of using power-to-liquid plants for power storage purposes. In: 2016 13th International Conference on the European Energy Market (EEM), S03_10163. IEEE Xplore Digital Library
- König, D, Freiberg, M Dietrich, R.-U. Wörner, A (2015) Techno-economic study of the storage of fluctuating renewable energy in liquid hydrocarbons. Fuel – The Science and Technology of Fuel and Energy, 159:289-297


